Tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate: A Versatile Compound for Organic Synthesis
Introduction
Tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate is a chemical compound that finds extensive use in organic synthesis. This compound belongs to the ester family and possesses unique characteristics that make it a valuable building block for the preparation of various organic compounds. This article explores the properties, synthesis methods, and diverse applications of tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate in the field of organic chemistry.
Properties and Structure
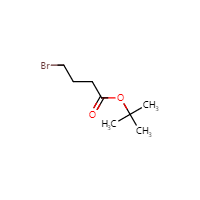
Tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate, also known as t-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate or 4-Bromo-2-methylpropanoic acid tert-butyl ester, has the molecular formula C8H15BrO2. Its structure consists of a butanoate (C4H7O2) group attached to a tert-butyl (C4H9) group through an ester linkage. The presence of the bromine atom (Br) adds further reactivity and versatility to the compound.
Synthesis Methods
Several methods are available for the synthesis of tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate. One common approach involves the reaction of tert-butyl alcohol with 4-bromobutanoic acid in the presence of a dehydrating agent such as thionyl chloride or phosphorus pentachloride. The reaction proceeds via esterification, resulting in the formation of tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate as a colorless liquid with a characteristic fruity odor.
Applications in Organic Synthesis
Building Block for Pharmaceutical Compounds: Tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate serves as a versatile building block in the synthesis of various pharmaceutical compounds. It can undergo substitution reactions, nucleophilic additions, and cross-coupling reactions to introduce diverse functional groups and structural motifs into target molecules. Its reactivity allows for the creation of complex molecular architectures.
Agrochemical Synthesis: The compound's bromine atom provides a site for further functionalization, making tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate useful in the synthesis of agrochemicals such as herbicides, insecticides, and fungicides. By modifying the bromine substituent, chemists can tailor the compound's properties to meet specific agricultural needs.
Organic Intermediates: Tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate serves as a valuable intermediate in the synthesis of various organic compounds. It can be converted into different functionalized esters, acids, alcohols, or amines through diverse chemical reactions. This flexibility allows chemists to access a wide range of organic building blocks for further transformations.
Material Science: The reactivity of tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate makes it suitable for polymerization reactions, leading to the formation of polymeric materials with tailored properties. By incorporating this compound into polymer backbones, researchers can introduce specific functionalities, improve mechanical properties, or enhance biocompatibility.
Conclusion
Tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate plays a vital role in organic synthesis, offering versatility, reactivity, and synthetic accessibility. Its ester functionality and bromine substituent make it a valuable building block for the preparation of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, organic intermediates, and polymeric materials. As chemists continue to explore novel synthetic strategies, tert-Butyl 4-Bromobutanoate will remain a valuable tool in the toolbox of organic synthesis.
评论
发表评论